Blog
Optimizing Architectural Design in IBS Construction: A Comprehensive Guide


Optimizing Architectural Design in IBS Construction: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Embracing IBS Construction
- Understanding IBS and Its Benefits
- Key Considerations for Architectural Design in IBS Construction 3.1 Designing for Modular Components 3.2 Ensuring Structural Integrity 3.3 Integration of Services and Utilities 3.4 Flexibility and Future Adaptability 3.5 Emphasizing Aesthetics in Modular Design
- Collaborative Design Approach 4.1 Engaging Stakeholders Early in the Process 4.2 Leveraging Building Information Modeling (BIM) 4.3 Integrating Design and Manufacturing 4.4 Continuous Iteration and Improvement
- Sustainability and Green Building Practices 5.1 Energy Efficiency in IBS Design 5.2 Material Selection and Waste Reduction 5.3 Optimal Space Planning and Natural Lighting 5.4 Incorporating Renewable Energy Systems
- Overcoming Challenges in IBS Architectural Design 6.1 Design Standardization vs. Customization 6.2 Regulatory Compliance and Approval Processes 6.3 Addressing Perception and Public Acceptance
- Case Studies: Successful Examples of Optimized IBS Architectural Design 7.1 Iconic IBS Buildings around the World 7.2 Residential Projects Showcasing Innovative Designs 7.3 Commercial and Industrial Structures Embracing IBS
- Technology and Automation in IBS Architectural Design 8.1 Utilizing AI and Machine Learning 8.2 Robotics in Prefabrication and Assembly 8.3 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Design Visualization
- Future Trends and Innovations in IBS Architectural Design 9.1 3D Printing of Building Components 9.2 Smart Buildings and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration 9.3 Biophilic Design in IBS Construction 9.4 Advancements in Sustainable Materials
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction: Embracing IBS Construction
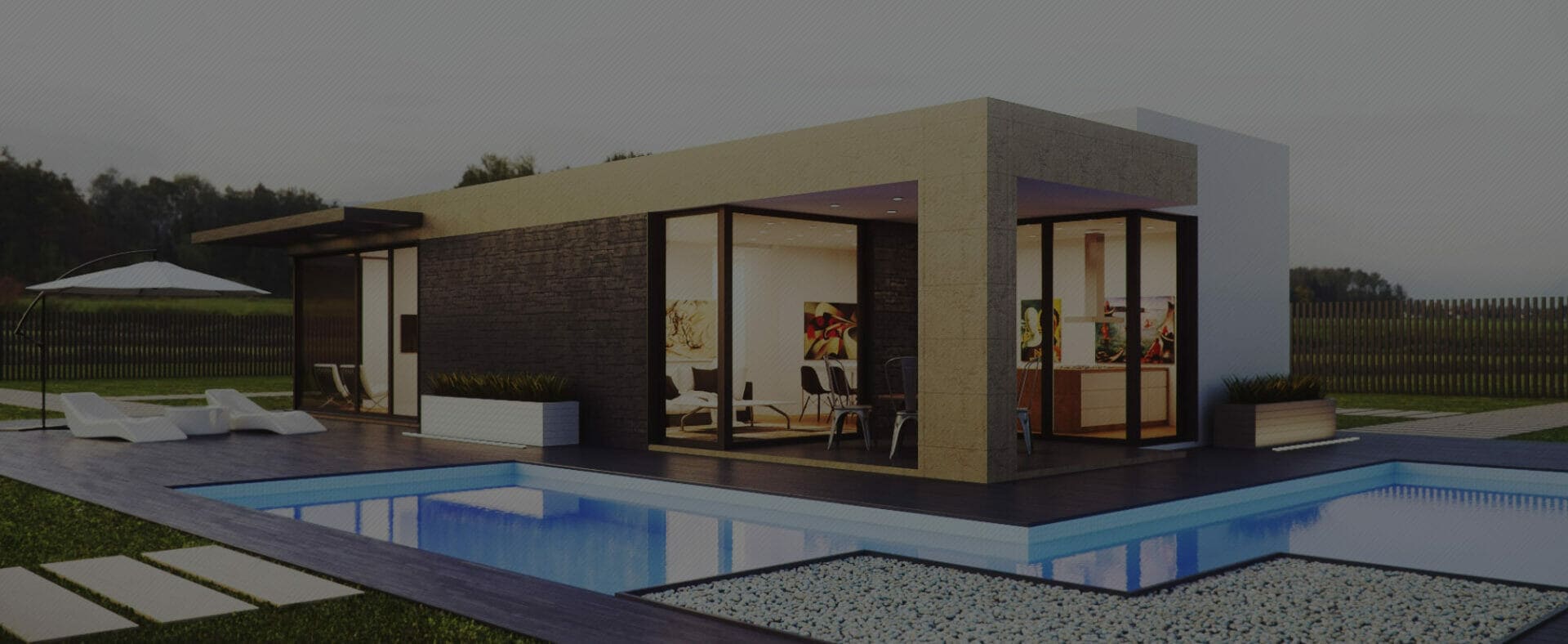
The construction industry is continually evolving, and one of the most significant advancements in recent years is the adoption of Industrialized Building Systems (IBS). IBS revolutionizes the way buildings are designed and constructed, offering numerous benefits such as faster construction, improved quality, and cost-effectiveness. To fully leverage the advantages of IBS, it is crucial to optimize the architectural design process. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of optimizing architectural design in IBS construction and provides valuable insights for architects and designers in this field.
2. Understanding IBS and Its Benefits
Before diving into the optimization of architectural design, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of IBS and its benefits. IBS construction involves the prefabrication of building components in a controlled factory environment, which are then transported to the construction site for assembly. The benefits of IBS construction include accelerated project timelines, enhanced quality control, reduced labor costs, and minimized environmental impact.
3. Key Considerations for Architectural Design in IBS Construction
To optimize architectural design in IBS construction, several key considerations should be taken into account.
3.1 Designing for Modular Components
One of the fundamental principles of IBS construction is the use of modular components. Designers must understand the modular nature of IBS and create designs that align with this approach. By designing with modules in mind, architects can maximize efficiency, minimize wastage, and streamline the assembly process.
3.2 Ensuring Structural Integrity
Structural integrity is crucial in any construction project, and IBS is no exception. Architects must ensure that their designs meet all structural requirements and can withstand various loads and forces. Collaboration with structural engineers is essential to achieve optimal structural integrity in IBS construction.
3.3 Integration of Services and Utilities
Effective integration of services and utilities within an IBS structure requires careful planning during the design phase. Architects must consider the placement of electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems to ensure seamless integration with the modular components. This integration enhances the functionality and efficiency of the building.
3.4 Flexibility and Future Adaptability
Designing for flexibility and future adaptability is vital in IBS construction. Buildings should be designed to accommodate potential changes or expansions in the future. This flexibility ensures long-term functionality and minimizes the need for costly modifications as needs evolve over time.
3.5 Emphasizing Aesthetics in Modular Design
Contrary to common perception, modular design does not limit architectural aesthetics. Architects can incorporate creative and visually appealing elements into the design of IBS structures. By exploring innovative modular solutions and finishes, architects can create visually stunning buildings that showcase the benefits of IBS construction.
4. Collaborative Design Approach
A collaborative approach is essential to optimize architectural design in IBS construction.
4.1 Engaging Stakeholders Early in the Process
Early involvement of stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and manufacturers, allows for a comprehensive understanding of project requirements. Collaboration from the initial design stages leads to better decision-making and efficient project execution. By engaging stakeholders early on, architects can gather valuable insights and ensure that the design aligns with the goals and constraints of all parties involved.
4.2 Leveraging Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) plays a crucial role in IBS architectural design. BIM software enables architects to create detailed 3D models, facilitating better visualization, clash detection, and coordination among various disciplines involved in the project. Leveraging BIM enhances communication and collaboration, streamlines the design process, and reduces errors and rework.
4.3 Integrating Design and Manufacturing
Seamless integration between design and manufacturing processes is essential in IBS construction. Architects must work closely with manufacturers to ensure that the design intent is effectively translated into the manufacturing and assembly of modular components. Collaboration between architects and manufacturers enables design optimization for manufacturability, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective construction.
4.4 Continuous Iteration and Improvement
The iterative design process is crucial in optimizing architectural design for IBS construction. Designers should continuously evaluate and improve their designs based on feedback from stakeholders, lessons learned from previous projects, and emerging industry trends. By embracing a mindset of continuous improvement, architects can refine their designs and adapt to changing requirements, ultimately delivering better outcomes in IBS construction projects.
5. Sustainability and Green Building Practices
Sustainability is a pressing concern in the construction industry, and IBS construction offers opportunities to embrace green building practices.
5.1 Energy Efficiency in IBS Design
Architects should prioritize energy efficiency in IBS design. This can be achieved by incorporating features such as insulation, efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. Energy modeling tools can help optimize energy consumption during the design phase, resulting in buildings that are environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate.
5.2 Material Selection and Waste Reduction
Careful material selection is crucial in IBS construction to ensure durability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. Architects should prioritize the use of sustainable materials with low environmental impact. Additionally, waste reduction strategies, such as efficient material usage and recycling, should be integrated into the design process to minimize waste generation.
5.3 Optimal Space Planning and Natural Lighting
Efficient space planning is essential in IBS architectural design to maximize the functionality and usability of the building. Architects should consider factors such as room layouts, traffic flow, and spatial optimization. Furthermore, incorporating natural lighting strategies through thoughtful window placement and skylights not only reduces energy consumption but also enhances the overall occupant experience and well-being.
5.4 Incorporating Renewable Energy Systems
IBS structures provide excellent opportunities for integrating renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines. Architects should explore these options during the design phase to optimize the energy performance of the building and reduce its carbon footprint. By harnessing renewable energy sources, IBS buildings can contribute to a more sustainable future.
6. Overcoming Challenges in IBS Architectural Design
While IBS construction offers numerous benefits, there are challenges that architects must address.
6.1 Design Standardization vs. Customization
Finding the right balance between design standardization and customization is crucial in IBS construction. Standardization improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enables faster construction. However, customization allows architects to meet specific client requirements and create unique buildings. Architects must carefully consider project-specific factors and strike a balance that meets both functional and aesthetic needs.
6.2 Regulatory Compliance and Approval Processes
Architects must navigate regulatory frameworks and approval processes when designing IBS structures. Compliance with local building codes and regulations ensures the safety and legality of the construction. Architects should stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and work closely with regulatory authorities to ensure compliance throughout the design and construction phases.
6.3 Addressing Perception and Public Acceptance
The perception of IBS construction can be a challenge, as it is relatively new in many regions. Architects need to educate clients and the public about the benefits and capabilities of IBS, fostering acceptance and trust in this innovative construction method. Clear communication and showcasing successful case studies can help overcome skepticism and build confidence in IBS architectural design.
7. Case Studies: Successful Examples of Optimized IBS Architectural Design
Examining successful case studies can provide valuable insights into the potential of IBS architectural design.
7.1 Iconic IBS Buildings around the World
Explore iconic buildings around the world that showcase the possibilities of IBS construction. These structures exemplify the combination of aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability in IBS architectural design. From residential towers to commercial complexes, these projects demonstrate the diverse applications and benefits of IBS.
7.2 Residential Projects Showcasing Innovative Designs
Residential projects offer excellent opportunities for optimized IBS architectural design. Discover innovative designs that prioritize comfort, energy efficiency, and flexible living spaces. These projects demonstrate how IBS can be tailored to meet the unique needs of homeowners while delivering a superior living experience.
7.3 Commercial and Industrial Structures Embracing IBS
The commercial and industrial sectors have also embraced IBS construction. Learn about projects that demonstrate the advantages of IBS in terms of speed, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability to different functions. From office buildings to manufacturing facilities, these examples highlight the potential of IBS in creating efficient and functional spaces for business operations.
8. Technology and Automation in IBS Architectural Design
Technology and automation play an increasingly important role in optimizing architectural design in IBS construction.
8.1 Utilizing AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies can enhance the design process by analyzing vast amounts of data and generating insights. Architects can leverage AI and ML algorithms to optimize building performance, streamline design iterations, and improve decision-making.
8.2 Robotics in Prefabrication and Assembly
Robotic systems have transformed the prefabrication and assembly processes in IBS construction. Robots can automate repetitive tasks, improve precision, and accelerate construction timelines. Architects should explore the integration of robotics into the design and manufacturing processes to unlock the full potential of IBS.
8.3 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Design Visualization
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies offer immersive design visualization experiences. Architects can use VR and AR to walk through virtual building models, evaluate spatial relationships, and test design concepts. These technologies enhance communication and collaboration among stakeholders and enable better design decision-making.
9. Future Trends and Innovations in IBS Architectural Design
The future of IBS architectural design holds exciting possibilities. Several trends and innovations are shaping the evolution of IBS construction.
9.1 3D Printing of Building Components
3D printing is revolutionizing the construction industry, enabling the fabrication of complex building components with precision and efficiency. Architects can explore the potential of 3D printing to create customized and intricate designs while reducing material wastage and construction time.
9.2 Smart Buildings and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The rise of smart buildings and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies offer new opportunities for IBS architectural design. Architects can incorporate IoT devices and sensors into IBS structures to enable intelligent building management systems, optimize energy consumption, and enhance occupant comfort.
9.3 Biophilic Design in IBS Construction
Biophilic design emphasizes the integration of nature into the built environment, promoting health and well-being. Architects can incorporate biophilic design principles into IBS construction, integrating natural elements such as green walls, daylighting, and outdoor spaces to create harmonious and sustainable buildings.
9.4 Advancements in Sustainable Materials
The development of sustainable materials is a significant area of innovation in IBS architectural design. Architects can explore the use of eco-friendly materials, such as recycled or bio-based materials, to enhance the environmental performance of IBS structures. Advancements in sustainable materials contribute to the overall sustainability goals of IBS construction.
10. Conclusion
Optimizing architectural design in IBS construction is crucial to fully leverage the benefits of this innovative construction method. By considering modular design principles, embracing a collaborative approach, integrating sustainability practices, and adopting emerging technologies, architects can create remarkable structures that meet client requirements while contributing to a more efficient and sustainable built environment. The future of IBS architectural design holds immense potential, and by staying informed, adaptable, and creative, architects can shape the future of construction.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: Is IBS construction suitable for all types of buildings?
Yes, IBS construction can be adapted to various types of buildings, including residential, commercial, and industrial structures. However, the specific design considerations may vary depending on the building’s purpose and requirements.
FAQ 2: How does IBS construction contribute to sustainability?
IBS construction promotes sustainability by reducing material wastage, minimizing construction time, and improving energy efficiency. It allows for better control over the construction process, resulting in higher-quality buildings with a reduced environmental impact.
FAQ 3: Are IBS structures aesthetically pleasing?
Absolutely! IBS structures can be designed to be visually appealing and architecturally stunning. With careful planning and creative use of modular components, architects can create beautiful and unique buildings that showcase the benefits of IBS construction.
FAQ 4: What are the cost implications of IBS construction?
While initial costs may be higher compared to traditional construction methods, IBS construction offers long-term cost savings through reduced labor requirements, faster project completion, and improved building performance. It is essential to consider the life cycle costs when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of IBS.
FAQ 5: How can architects stay updated with the latest trends in IBS architectural design?
Architects can stay updated with the latest trends in IBS architectural design by actively participating in industry conferences, workshops, and networking events. They can also engage in continuous learning and professional development to expand their knowledge and skills in this evolving field.